In the rapidly growing Indian solar market, the choice between poly and mono cells holds significant importance for investors and consumers alike. As solar energy continues to gain traction as a sustainable power source, understanding the nuances and distinctions between these two cell types becomes essential. In this article, we will provide a detailed comparison of poly and mono cells, focusing specifically on their relevance and performance in the Indian solar market.
Poly vs. Mono Cells: Understanding the Fundamentals Poly-crystalline (poly) and mono-crystalline (mono) cells are two prevalent types of solar cells used in the Indian market. Both are constructed using silicon, a highly efficient semiconductor material. However, their manufacturing processes result in differing efficiency levels, aesthetics, and cost considerations.
- Poly-Crystalline (Poly) Cells: Poly cells are manufactured by melting multiple fragments of silicon together, forming a solid block which is then cut into wafers. This method allows for a less precise production process, giving poly cells a distinctive blue appearance. While poly cells offer a lower conversion efficiency compared to mono cells, they are more cost-effective, making them a popular choice for large-scale installations in India.
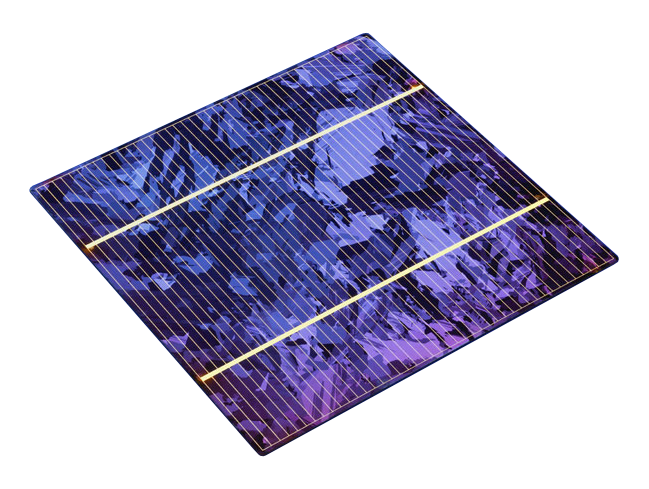
- Mono-Crystalline (Mono) Cells: Mono cells, on the other hand, are made from a single, high-purity silicon crystal. This manufacturing technique ensures a higher level of uniformity and efficiency, resulting in a sleek black appearance. Mono cells tend to have a higher conversion efficiency, making them an excellent choice for installations with limited space and a preference for aesthetics in the Indian market.
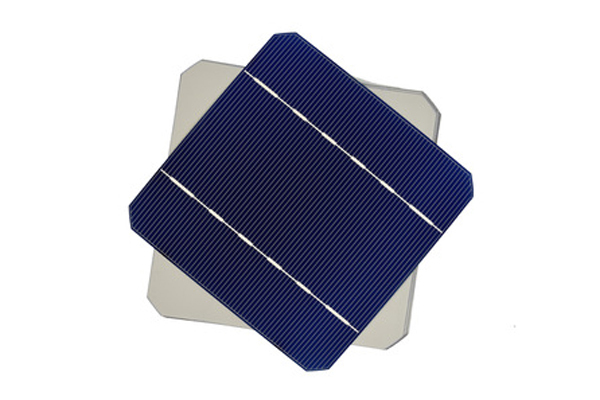
Comparing Efficiency and Performance: Efficiency plays a vital role in determining the viability and productivity of solar installations. Mono cells, with their uniform structure, outperform poly cells in terms of conversion efficiency. Typically, mono cells achieve efficiencies ranging from 18% to 23%, while poly cells typically achieve efficiencies between 15% and 18%.
Furthermore, mono cells exhibit superior performance under low-light conditions, making them a favorable choice for regions in India with limited direct sunlight. Conversely, poly cells may experience a slight decrease in output when exposed to partial shading or indirect light.
Considering Cost Factors: Cost considerations are crucial when deciding on the most suitable solar cell type for projects in the Indian market. Poly cells have an advantage in terms of affordability. The simplified manufacturing process for poly cells leads to lower production costs, making them an attractive option for utility-scale solar projects where cost-effectiveness is a primary concern.
Mono cells, despite their higher efficiency, tend to be more expensive due to the manufacturing process involved. However, advancements in technology and increasing demand have led to a gradual reduction in the price gap between mono and poly cells in recent years.
When making a decision between poly and mono cells in the Indian solar market, it is crucial to consider factors such as efficiency, performance under varying light conditions, and cost. While mono cells offer higher conversion efficiency and better performance under low-light scenarios, poly cells provide a cost-effective solution for large-scale installations. The choice ultimately depends on project-specific requirements and budget considerations.
By thoroughly understanding the differences and advantages of poly and mono cells, stakeholders in the Indian solar market can make well-informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals and financial objectives.


wpm3hr